Both Cardano (ADA) and Solana (SOL) are high-performing Layer-1 blockchains with unique goals and trade-offs. Cardano emphasizes scientific rigor, decentralization, and sustainability, while Solana focuses on speed, scalability, and mass adoption.
⚙️ Quick Comparison Table
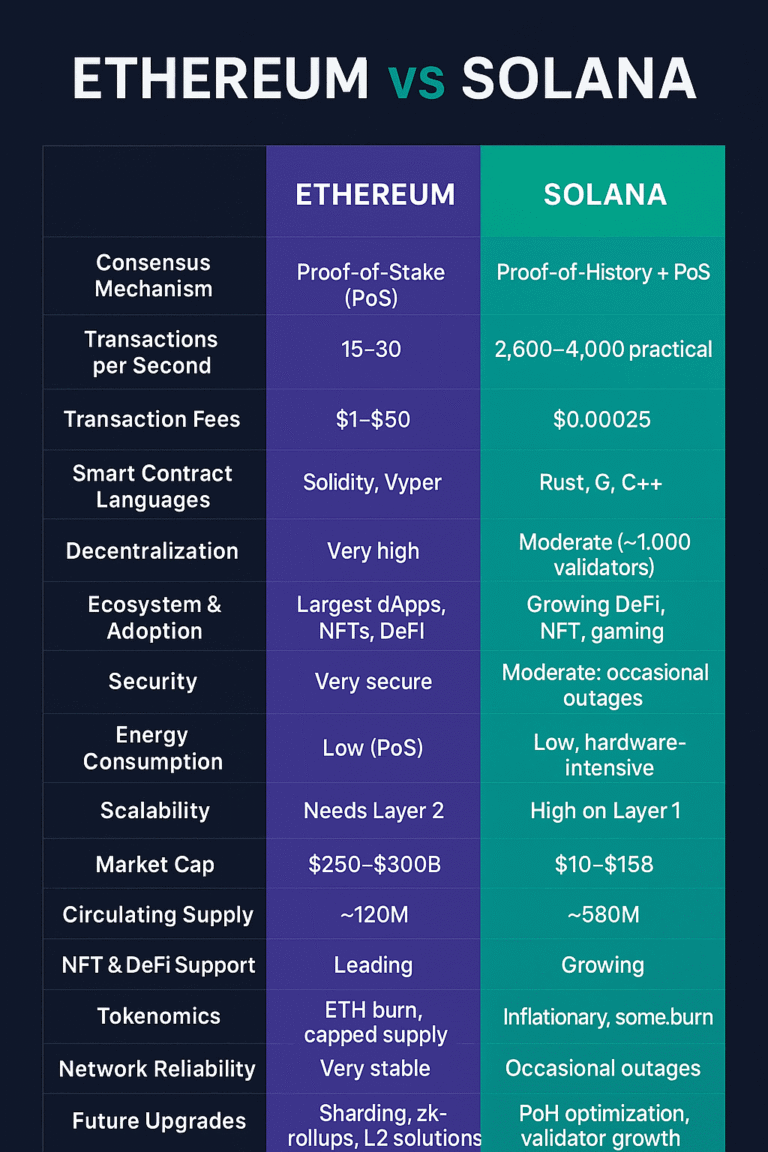
| # | Parameter | Cardano (ADA) | Solana (SOL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Consensus Mechanism | Ouroboros Proof of Stake (PoS) | Proof of History (PoH) + Proof of Stake |
| 2 | Transaction Speed (TPS) | ~250–1,000 (Hydra → 1M+) | Up to 65,000 |
| 3 | Finality / Latency | 10–60 sec | 1–2 sec |
| 4 | Transaction Fees | ~$0.20 | <$0.01 |
| 5 | Smart Contract Language | Plutus (Haskell-based) | Rust, C, C++ |
| 6 | Architecture | Dual-layer (Settlement + Computation) | Monolithic (Layer-1) |
| 7 | Decentralization | 3,000+ independent stake pools | ~2,000 validators, higher hardware needs |
| 8 | Security | Peer-reviewed, formally verified | High-speed but prone to outages |
| 9 | Ecosystem & dApps | Moderate; academic projects | Large, fast-growing DeFi & NFT ecosystem |
| 10 | DeFi TVL (2025 est.) | ~$300M | ~$4B+ |
| 11 | Tokenomics | Fixed supply (45B ADA) | Inflationary (no hard cap) |
| 12 | Energy & Hardware Needs | Low, eco-friendly | High-end hardware, energy-intensive |
| 13 | Network Stability | Excellent uptime | Occasional outages under load |
| 14 | Adoption / Active Users | Moderate, growing | Very high, strong community |
| 15 | Innovation Pace | Steady, peer-reviewed | Rapid, experimental |
| 16 | Risk Profile | Low-risk, slower adoption | High-risk, high reward |
🧩 Detailed Comparison by Parameter
1. Consensus Mechanism
Cardano: Uses Ouroboros Proof of Stake (PoS) — the first academically peer-reviewed consensus protocol. It selects validators (slot leaders) proportionally to their stake, ensuring fairness and energy efficiency.
Solana: Utilizes Proof of History (PoH) combined with PoS. PoH timestamps transactions, ordering them efficiently before they enter the PoS validation process, greatly increasing throughput.
2. Transaction Speed (TPS)
Cardano: Current network capacity handles ~250–1,000 TPS, depending on node configuration. The upcoming Hydra Layer-2 aims for up to 1 million TPS theoretically.
Solana: One of the fastest L1s, processing up to 65,000 TPS under optimal conditions thanks to PoH and parallel execution (Sealevel).
3. Transaction Finality / Latency
Cardano: Finality is achieved after several confirmations — usually 10–60 seconds.
Solana: Achieves near-instant finality, typically within 1–2 seconds.
4. Transaction Fees
Cardano: Transaction fees are deterministic and average around $0.10–$0.30.
Solana: Fees are extremely low, typically less than $0.01 due to high throughput and optimized design.
5. Smart Contract Language
Cardano: Uses Plutus, a Haskell-based language emphasizing formal verification — mathematically proving contract correctness and security.
Solana: Supports Rust, C, and C++, offering broader developer accessibility and performance optimization.
6. Architecture & Layer Design
Cardano: Has a dual-layer architecture — the Settlement Layer handles ADA transactions, while the Computation Layer manages smart contracts. This modular structure aids scalability and future upgrades.
Solana: Operates as a monolithic Layer-1, where consensus, execution, and settlement happen in one layer — allowing speed but less flexibility.
7. Decentralization
Cardano: Over 3,000+ stake pools, making it one of the most decentralized networks globally.
Solana: Around 2,000 validators, but many rely on powerful servers and cloud infrastructure, increasing centralization risk.
8. Security
Cardano: Employs formal methods and peer-reviewed cryptography. Designed to minimize attack vectors.
Solana: Technically secure but has suffered network outages and bot attacks, indicating operational vulnerabilities.
9. Ecosystem & dApps
Cardano: Ecosystem includes DeFi, identity management, and education initiatives (e.g., Atala Prism in Ethiopia). Growth is slow but steady.
Solana: Massive ecosystem with top projects like Jupiter, Raydium, Magic Eden, Tensor, and Helium. It attracts both developers and retail users.
10. Total Value Locked (TVL)
Cardano: As of 2025, TVL is around $250–300 million.
Solana: TVL exceeds $4 billion, supported by vibrant DeFi and staking projects.
11. Tokenomics
Cardano: Fixed supply of 45 billion ADA, ensuring scarcity and predictable monetary policy. Inflation declines as staking stabilizes.
Solana: No hard cap; current inflation around 1.5% annually, with partial fee burning to offset supply growth.
12. Energy & Hardware Requirements
Cardano: Very energy-efficient and accessible — nodes can run on modest hardware (e.g., Raspberry Pi).
Solana: Requires high-performance servers (multi-core CPUs, 128+ GB RAM, fast SSDs) due to intense data throughput.
13. Network Stability
Cardano: Rarely experiences downtime. Releases are carefully tested before deployment.
Solana: Has faced multiple outages (notably in 2021–2024) due to spam attacks or software overload.
14. Adoption / Active Users
Cardano: ~1.5 million active wallets, with a strong staking community.
Solana: Tens of millions of active wallets, massive NFT market, and retail usage.
15. Innovation Pace
Cardano: Slow, research-driven roadmap — every upgrade (like Hydra, Voltaire, Basho) goes through formal review.
Solana: Rapid iteration — features like Firedancer (new validator client) aim to boost decentralization and throughput.
16. Risk Profile
Cardano: Low risk due to strong fundamentals, slow but steady growth, and academic rigor.
Solana: High risk–high reward. Rapid innovation, but potential instability and centralization risks.
🧠 Final Summary
Security, Stability, Decentralization
🟢 Cardano
Speed, Fees, Ecosystem Activity
🔵 Solana
Long-Term Sustainability
🟢 Cardano
Innovation & Adoption Speed
🔵 Solana
🏁 Conclusion
Cardano represents a measured, scientifically grounded approach to blockchain evolution — ideal for investors and developers prioritizing stability, governance, and long-term sustainability.
Solana, on the other hand, embodies speed, innovation, and mass adoption, making it perfect for real-time applications like DeFi, gaming, and NFTs — though it comes with operational risks.
In short:
🔹 Cardano = Security & Decentralization
🔹 Solana = Speed & Adoption
Both are vital pillars of the blockchain landscape — one building trust through science, the other scaling the future through technology.
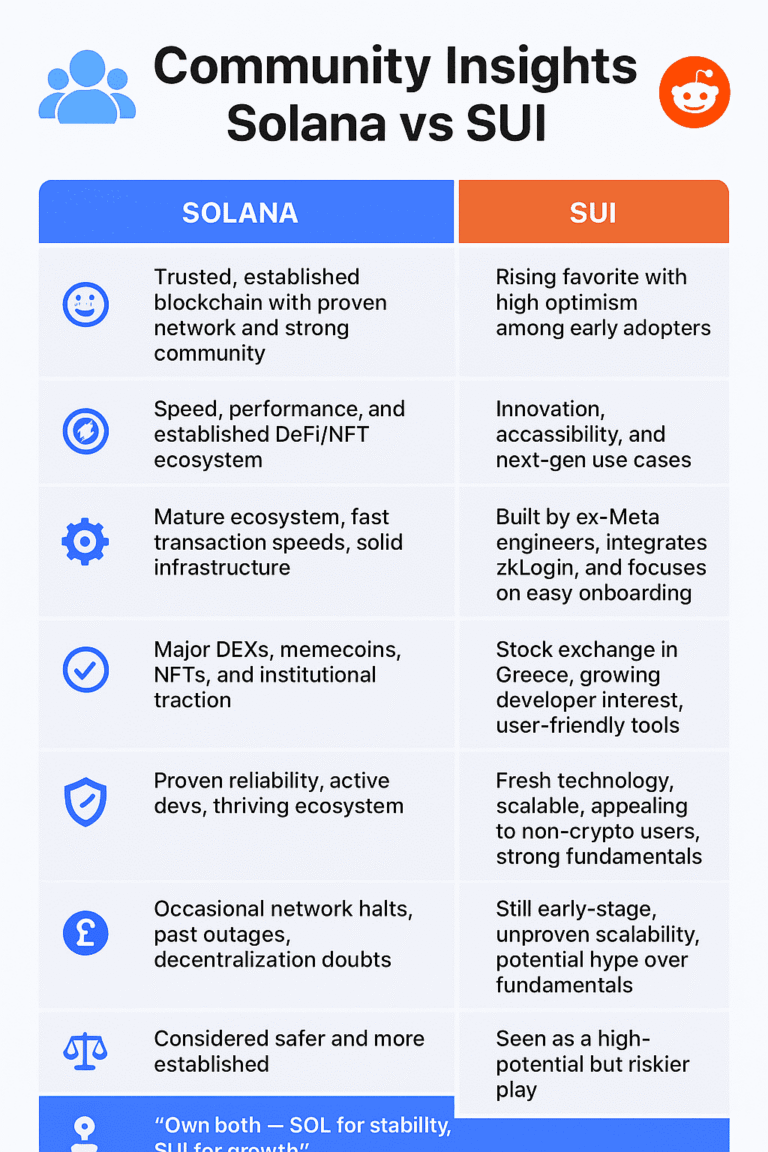
💬 What People Say / Community Take
Here’s how the community usually compares Cardano and Solana — and what people are really saying about both:
💡Cardano — “the slow but steady one”
- ▹ People respect Cardano for being methodical and research-driven — it’s often called the “academic blockchain.”
- ▹ It’s seen as reliable and stable, with few network issues and a strong focus on decentralization.
- ▹ Many appreciate that anyone can run a node without expensive hardware, which makes the network feel more community-led.
- ▹ The main critique? It’s slow to roll out features, and some say its ecosystem isn’t growing as fast as competitors.
⚡Solana — “the fast and fearless one”
- ▹ Solana gets praised for blazing speed and dirt-cheap transactions, which attract DeFi apps, NFT projects, and retail users.
- ▹ The ecosystem moves fast — developers love how quickly they can build and deploy.
- ▹ But users often mention network outages and high validator costs, raising concerns about long-term decentralization.
- ▹ It’s viewed as exciting and innovative — but sometimes a bit “move fast, break things.”
🤝The middle ground
- ▹ Many users now say it’s not about Cardano vs. Solana, but how both can coexist — Cardano for long-term reliability, Solana for high-speed experimentation.
- ▹ On forums like Reddit, the tone feels less like rivalry and more like different philosophies serving different goals.